-
![LANG-CODE-KEY]() LANG_NAME_KEY
LANG_NAME_KEY
Account created: .

Awarded for destroying at least 17 aerial targets in a single sortie and winning the battle.

Awarded for destroying at least 10 aerial targets in a single sortie and winning the battle.
The destroyed targets must include aircraft of all 5 types.

Awarded for earning the highest aircraft type grade in battle.

Awarded for destroying an aerial target using a rocket.

Awarded for destroying at least 20 aircraft from the enemy combat group.

Awarded for earning at least 5000 personal points in each of at least 2 battles played in a row.
The count is reset if the player earns fewer than 5000 personal points in a single battle.

Awarded to members of a Flight that destroyed at least 25 aerial targets.
The count is reset if one of the Flight members is destroyed.

Awarded for destroying an aerial target aircraft by setting it on fire.
Available once for each aircraft in the Hangar.

Awarded once for destroying an aircraft from an Attack Flight.
| Battles Fought | 1,835 |
| Victories | 1,151 (62.72%) |
| Draws | 9 (0%) |
| Defeats | 675 (37%) |
| Average Experience per Battle | 1,314 |
| Maximum Experience per Battle | 5,328 |
| Aerial Targets Destroyed | 3.01 |
| Ground Targets Destroyed | 0.78 |
| Damage Caused to Aerial Targets | 687.56 |
| Damage Caused to Ground Targets | 2,689.16 |
| Fighters | 1,049 (56%) |
| Multirole Fighters | 209 (11%) |
| Heavy Fighters | 123 (7%) |
| Attack Aircraft | 81 (4%) |
| Bombers | 403 (22%) |
| U.S.S.R. Aircraft | 461 (25%) |
| Germany Aircraft | 420 (23%) |
| U.S.A. Aircraft | 278 (15%) |
| Japan Aircraft | 283 (15%) |
| U.K. Aircraft | 371 (20%) |
| China Aircraft | 9 (0%) |
| Europe Aircraft | 43 (2%) |
| Ratings | Value | Place | |
| Aircraft | Total Sorties | Selected at the Start of a Battle | Most Aerial Targets Destroyed per Sortie | Most Ground Targets Destroyed per Sortie | ||||||||||||||||
| Fighters 82 | 2,183 | 1,024 | ||||||||||||||||||
|
II

Nakajima A4N
Nakajima A4N
|
14 | 8 | 12 | 0 | ||||||||||||||||
|
Used widely during the Second Sino-Japanese War. The last biplane designed by Nakajima. Aircraft Description
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
II

Kawasaki Ki-5
Kawasaki Ki-5
|
2 | 1 | 5 | 0 | ||||||||||||||||
|
Designed in Japan under the guidance of German experts. A total of 4 prototypes were built and underwent trials in 1934. Aircraft Description
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
II

Nakajima Ki-8
Nakajima Ki-8
|
5 | 3 | 7 | 0 | ||||||||||||||||
|
Designed for the Imperial Japanese Army Air Force in 1933–1935. A total of 5 prototypes were built. Never entered service. Aircraft Description
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
II

TsKB I-7
TsKB I-7
|
1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | ||||||||||||||||
|
Developed in Germany by the Heinkel firm under the designation HD-37. Saw mass production in the U.S.S.R. as the I-7. Aircraft Description
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
II

Curtiss XP-31
Curtiss XP-31
|
103 | 53 | 23 | 0 | ||||||||||||||||
|
Developed in 1932–1933 for the U.S. Army. One prototype was built, but the aircraft never entered service. Aircraft Description
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
II
Blériot-SPAD S.510
Blériot-SPAD S.510
|
10 | 5 | 13 | 0 | ||||||||||||||||
|
First flew in January 1933. Served until 1940. Never saw combat. A total of about 60 aircraft were built. Aircraft Description
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
II

Focke-Wulf Fw 56 Stosser
Focke-Wulf Fw 56 Stosser
|
2 | 1 | 12 | 0 | ||||||||||||||||
|
One of the first designs of a fighter aircraft for the reviving Luftwaffe. The aircraft featured a parasol wing. Aircraft Description
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
II

Arado Ar 67
Arado Ar 67
|
8 | 6 | 13 | 0 | ||||||||||||||||
|
Developed to replace the Ar 65. First flew in the fall of 1933. Being outperformed by the competing Ar 68, it never entered service. Aircraft Description
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
III

Mitsubishi Ki-33
Mitsubishi Ki-33
|
2 | 1 | 8 | 0 | ||||||||||||||||
|
Performed trials in 1936 as a new fighter for the Japanese Army. Two prototypes were built. Aircraft Description
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
III

Nakajima Ki-27
Nakajima Ki-27
|
8 | 4 | 13 | 0 | ||||||||||||||||
|
Developed to replace the Ki-10. The prototype first flew in October 1936. Saw combat in China, during the Battle of Khalkhyn Gol, and in the initial period of the Pacific War. A total of about 3,400 aircraft were built. Aircraft Description
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
III

Supermarine Type 224
Supermarine Type 224
|
35 | 21 | 19 | 0 | ||||||||||||||||
|
First flew in February 1934. The experience gained during the Type 224 development was subsequently used to create the famous Spitfire. Aircraft Description
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
III

Hawker P.V.3
Hawker P.V.3
|
28 | 17 | 13 | 0 | ||||||||||||||||
|
The Hawker P.V.3 was developed as an enlarged version of the Hawker Fury fighter powered by a new engine with an enhanced armament of four machine guns. The single completed prototype was tested with several variants of the Goshawk engines in 1934–1935. Aircraft Description
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
III

Breda Ba.27 Metallico
Breda Ba.27 Metallico
|
1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | ||||||||||||||||
|
Designed as a high-speed monoplane fighter for the Italian Air Force, the Ba.27M was not accepted into service and so was offered for export. Employed by the Chinese Air Force during the Second Sino-Japanese War. Aircraft Description
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
III

Boeing YP-29
Boeing YP-29
|
1 | 1 | 2 | 0 | ||||||||||||||||
|
Designed as an attempt of the Boeing company to produce a more advanced version of the successful P-26 Peashooter. A total of 4 prototypes were built. Aircraft Description
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
III

Polikarpov I-15bis DM-2
Polikarpov I-15bis DM-2
|
20 | 12 | 12 | 0 | ||||||||||||||||
|
Modification of the serial I-15 with ramjet engines for better climbing performance. Tested in 1939–1940. Aircraft Description
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
III

Avia Bk-534
Avia Bk-534
|
5 | 3 | 7 | 0 | ||||||||||||||||
|
A modification of the serial B-534 fighter with more powerful weapons. Due to the lack of 20 mm autocannons, only a small part of the Bk-534 was equipped with them regularly. Aircraft Description
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
III

Avia B-534
Avia B-534
|
8 | 3 | 12 | 0 | ||||||||||||||||
|
The main Czechoslovakian fighter of the 1930s. Later, the Luftwaffe, Slovak, and Bulgarian Air Forces also used these aircraft. It was last used for a military operation during the Slovak National Uprising in 1944. Aircraft Description
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
III

Brewster F2A-1 Buffalo
Brewster F2A-1 Buffalo
|
1 | 1 | 2 | 0 | ||||||||||||||||
|
Early version of the F2A Buffalo. A total of 11 aircraft of this modification were built for the U.S. Navy. Aircraft Description
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
IV

Seversky 2PA
Seversky 2PA
|
2 | 1 | 2 | 0 | ||||||||||||||||
|
Developed on the basis of the P-35 as a two-seat bomber escort fighter. Never entered service despite good flight performance. Aircraft Description
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
IV

Curtiss XP-36F Hawk
Curtiss XP-36F Hawk
|
5 | 2 | 8 | 0 | ||||||||||||||||
|
One of the mass-produced P-36As was experimentally redesigned into a version with heavy cannon armament. Following a cycle of tests, it was decided to revert to the initial version with machine gun armament. Aircraft Description
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
IV

Curtiss Model 81A-1
Curtiss Model 81A-1
|
1 | 1 | 2 | 0 | ||||||||||||||||
|
Early modification of the P-40, also known as the Curtiss Model 81A-1. A total of 199 aircraft of this modification were built. Aircraft Description
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
IV

Curtiss P-36C Hawk
Curtiss P-36C Hawk
|
1 | 1 | 2 | 0 | ||||||||||||||||
|
One of the early modifications of the P-36 Hawk. A total of 30 aircraft of this modification were built. Aircraft Description
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
IV

Polikarpov I-17
Polikarpov I-17
|
41 | 16 | 16 | 0 | ||||||||||||||||
|
Developed in 1934–1937, but never entered service due to lack of advantage over the mass-produced I-16. Only prototypes were built. Aircraft Description
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
IV

Curtiss P-36 Hawk
Curtiss P-36 Hawk
|
2 | 1 | 4 | 0 | ||||||||||||||||
|
One of the most successful fighters of the prewar period. Served in the air forces of the United States, Great Britain, France, the Netherlands, Norway, and China. Aircraft Description
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
IV

Grumman XF4F-3
Grumman XF4F-3
|
2 | 1 | 7 | 0 | ||||||||||||||||
|
Underwent trials in 1939. Improved version of the fighter entered service with the U.S. Navy as the F4F Wildcat. Aircraft Description
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
IV

Polikarpov I-153P DM-4
Polikarpov I-153P DM-4
|
1 | 1 | 3 | 0 | ||||||||||||||||
|
The mass-produced I-153P "Chaika" (a variant with two ShVAK cannons instead of 4 machine guns) was fitted with additional DM-4 ramjet engines. During the trials, a significant increase in the top speed was achieved. However, it was decided to continue work on the ramjet engines on newer types of aircraft. Aircraft Description
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
IV

Polikarpov I-153 DM-4
Polikarpov I-153 DM-4
|
8 | 3 | 5 | 0 | ||||||||||||||||
|
In October 1940, the mass-produced I-153 was experimentally fitted with auxiliary ramjet DM-4 engines. During the trials, a significant increase in the top speed was achieved. However, it was decided to continue work on the ramjet engines on newer types of aircraft. Aircraft Description
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
IV

Nakajima Ki-43-I Hayabusa
Nakajima Ki-43-I Hayabusa
|
73 | 38 | 16 | 1 | ||||||||||||||||
|
Developed by the Nakajima Aircraft Company to replace the Ki-27 in the Japanese Air Force. First aircraft entered service in the fall of 1941. A total of about 6,000 Ki-43s of various versions were built and used on all fronts until the end of World War II. Aircraft Description
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
IV

Mitsubishi A6M1 Zero
Mitsubishi A6M1 Zero
|
178 | 84 | 18 | 0 | ||||||||||||||||
|
Early prototypes of the famous A6M Zero were equipped with Zuisei engines. First flew in April 1939. Aircraft Description
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
IV

Fairey Fantome
Fairey Fantome
|
9 | 6 | 13 | 0 | ||||||||||||||||
|
Developed for export to the Belgian Air Force. A total of 4 prototypes were built and underwent trials in Great Britain, Belgium, and the U.S.S.R. Aircraft Description
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
IV

Messerschmitt Bf 109 B
Messerschmitt Bf 109 B
|
2 | 2 | 10 | 0 | ||||||||||||||||
|
The winner of the contest to become the principal fighter aircraft with the Luftwaffe. Early modifications were used in Spain and in the initial period of World War II. Aircraft Description
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
IV

Heinkel He 112
Heinkel He 112
|
18 | 6 | 7 | 0 | ||||||||||||||||
|
Developed and tested in 1935 as a new fighter for the Luftwaffe. Exported to Spain, Japan, Hungary, and Romania. A total of 100 aircraft were built. Aircraft Description
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
IV

Bristol Type 146
Bristol Type 146
|
6 | 3 | 9 | 0 | ||||||||||||||||
|
Went through trials in 1938 as a new fighter for the Royal Air Force, but was considered inferior to the Hawker Hurricane and Supermarine Spitfire. Aircraft Description
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
IV

Caudron-Renault C.714
Caudron-Renault C.714
|
9 | 3 | 4 | 0 | ||||||||||||||||
|
Developed on the basis of the racing aircraft. Used during the French campaign of 1940. A total of about 90 aircraft were built. Aircraft Description
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
IV

Nakajima Ki-43-Ic
Nakajima Ki-43-Ic
|
6 | 3 | 7 | 0 | ||||||||||||||||
|
Several Ki-43 aircraft were captured by the Chinese Nationalist Air Force and the Chinese Communist Air Force after Japan's defeat in the Pacific War. They were operated in China during the ongoing civil war. Aircraft Description
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
V

Miles M.20
Miles M.20
|
4 | 3 | 5 | 0 | ||||||||||||||||
|
Designed as a simplified modification for mass production. Underwent trials in 1940–1941, but never entered service. Aircraft Description
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
V

Supermarine Spitfire I
Supermarine Spitfire I
|
236 | 109 | 20 | 0 | ||||||||||||||||
|
First flown in March 1938. Widely used during the Battle of Britain. Aircraft Description
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
V

Arsenal-Delanne AD 10C2
Arsenal-Delanne AD 10C2
|
21 | 7 | 7 | 0 | ||||||||||||||||
|
Development of this two-seat fighter with the tandem wing configuration was started by the Arsenal company in 1939. The prototype was completed during the occupation of France. The aircraft was tested in the summer of 1941, but it was decided not to put it into mass production. Aircraft Description
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
V

CAC CA-12 Boomerang
CAC CA-12 Boomerang
|
60 | 28 | 15 | 2 | ||||||||||||||||
|
Fighter designed and produced in Australia based on the CA-1 Wirraway. A total of 250 aircraft were built in 1942–1945. Aircraft Description
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
V

Supermarine Spitfire Mk Ia
Supermarine Spitfire Mk Ia
|
25 | 10 | 11 | 0 | ||||||||||||||||
|
The most advanced fighter of the Royal Air Force at the start of World War II. Widely used in the Dunkirk operation and the Battle of Britain. Aircraft Description
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
V

Vickers Venom
Vickers Venom
|
3 | 1 | 3 | 0 | ||||||||||||||||
|
Designed in 1935–1936 to meet a British Air Ministry specification for a new single-seat fighter. Aircraft Description
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
V

XFL-1 Airabonita
XFL-1 Airabonita
|
12 | 4 | 6 | 0 | ||||||||||||||||
|
Prototype carrier-based variant of the P-39 Airacobra, which first flew in May 1940. Tested as a new fighter for the U.S. Navy, but was considered inferior to the F4U Corsair. Aircraft Description
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
V

Curtiss P-40 Warhawk
Curtiss P-40 Warhawk
|
14 | 8 | 13 | 0 | ||||||||||||||||
|
Developed on the basis of the P-36. Most extensively used against Japan during the Pacific War and in China, and on the Soviet-German front. Aircraft Description
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
V

Polikarpov I-180-3
Polikarpov I-180-3
|
8 | 4 | 12 | 0 | ||||||||||||||||
|
Third prototype of the I-180 fighter. Unlike its predecessors, the I-180-3 was equipped with weapons and engine intended by the design. The aircraft was viewed as a preproduction model, but the project was abandoned due to the cancelation of the I-180. Aircraft Description
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
V

Curtiss Tomahawk IIb
Curtiss Tomahawk IIb
|
1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | ||||||||||||||||
|
Modification of the Curtiss P-40. Served with the 1st American Volunteer Group (Flying Tigers) and was actively used in operations against Japan. Aircraft Description
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
V

Messerschmitt Bf 109 E Emil
Messerschmitt Bf 109 E Emil
|
134 | 63 | 17 | 0 | ||||||||||||||||
|
Modification of the Messerschmitt fighter created after military operations in Spain. Extensively used by the Luftwaffe and the air forces of German allies. Aircraft Description
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
V

Messerschmitt Bf 109 E-3
Messerschmitt Bf 109 E-3
|
39 | 19 | 10 | 0 | ||||||||||||||||
|
The most widely produced version of the Bf 109 E that was extensively used in the French campaign in 1940 and the Battle of Britain. A total of 1,868 aircraft were built. Aircraft Description
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
V

Heinkel He 100 D-1
Heinkel He 100 D-1
|
4 | 2 | 7 | 0 | ||||||||||||||||
|
Developed in the prewar period as an alternative to Messerschmitt fighters. Vied for the world speed record. Never entered service. Aircraft Description
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
V

Messerschmitt Me 209 V4
Messerschmitt Me 209 V4
|
22 | 15 | 9 | 0 | ||||||||||||||||
|
Blueprint created on the basis of the record-setting Me 209. The project was discontinued due to difficulties in maintenance of the uprated engine. Aircraft Description
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
V

Mitsubishi A6M3 (experimental)
Mitsubishi A6M3 (experimental)
|
109 | 46 | 15 | 0 | ||||||||||||||||
|
Several A6M3 were experimentally fitted with 30 mm Type 2 autocannon. However, the trials revealed that the recoil of the 30 mm autocannon was too strong. As a result, the intention to equip the mass-produced A6M with this autocannon was abandoned. Aircraft Description
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
V

Mikoyan-Gurevich MiG-3
Mikoyan-Gurevich MiG-3
|
23 | 9 | 13 | 0 | ||||||||||||||||
|
Developed in 1940 as a high-altitude, high-speed interceptor. Extensively used in 1941–1942. Over 3,000 aircraft were built. Aircraft Description
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
V

Yakovlev Yak-1
Yakovlev Yak-1
|
4 | 2 | 5 | 0 | ||||||||||||||||
|
Developed in 1940 as the I-26 high-speed fighter. One of the best Soviet fighters of the early years of World War II. A total of 8,734 aircraft of various modifications were produced. Aircraft Description
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
V

Lavochkin LaGG-3
Lavochkin LaGG-3
|
12 | 6 | 8 | 0 | ||||||||||||||||
|
Fighter constructed of timber and designed as a high-speed aircraft in the prewar period. Used on all fronts until the end of the war. Aircraft Description
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
V

Nakajima Ki-43-II Hayabusa
Nakajima Ki-43-II Hayabusa
|
8 | 3 | 5 | 0 | ||||||||||||||||
|
Military use of the first Ki-43 models revealed that the fighter lacked firepower, survivability, and top speed. To correct these faults, the Nakajima Aircraft Company developed a new modification that remained in production until the end of World War II. Aircraft Description
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
V
Mitsubishi A6M2 Zero
Mitsubishi A6M2 Zero
|
16 | 7 | 10 | 0 | ||||||||||||||||
|
Early in the Pacific War, the A6M was the world's most capable carrier-based fighter, which gave Japan air superiority. Aircraft Description
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
V

XP-77
XP-77
|
3 | 1 | 3 | 0 | ||||||||||||||||
|
Low-cost fighter developed to address the shortage of light-metal alloys used in aviation. Never entered service. Aircraft Description
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
VI

North American Mustang IA
North American Mustang IA
|
1 | 1 | 4 | 0 | ||||||||||||||||
|
Modification of the Mustang I that was supplied by the North American Aviation company to U.K. The aircraft featured powerful autocannon that replaced the machine guns fitted on the previous modification. A total of 93 aircraft of this modification were supplied to the Royal Air Force. Aircraft Description
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
VI
Supermarine Spitfire Vb IM
Supermarine Spitfire Vb IM
|
4 | 2 | 10 | 0 | ||||||||||||||||
|
A modification of the Spitfire V inspired by Iron Maiden. Aircraft Description
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
VI

Supermarine Spitfire Vb
Supermarine Spitfire Vb
|
2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | ||||||||||||||||
|
The Spitfire V modification Aircraft Description
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
VI

Supermarine Spitfire V
Supermarine Spitfire V
|
82 | 37 | 14 | 1 | ||||||||||||||||
|
Developed in 1941 to replace the Spitfire I and Spitfire II. Widely used in Europe and North Africa. Aircraft Description
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
VI

Yakovlev Yak-1M
Yakovlev Yak-1M
|
50 | 26 | 14 | 0 | ||||||||||||||||
|
Created in 1943 on the basis of the Yak-1. Further improvements led to creation of the Yak-3. Aircraft Description
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
VI

Lavochkin La-5
Lavochkin La-5
|
56 | 24 | 12 | 0 | ||||||||||||||||
|
A further development of the LaGG-3 featuring an air-cooled engine and enhanced aerodynamics. Aircraft Description
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
VI

P-39N-1 Airacobra
P-39N-1 Airacobra
|
45 | 20 | 16 | 0 | ||||||||||||||||
|
The developer was looking for ways to improve aircraft characteristics based on feedback from the pilots who flew various modifications of the P-39 Airacobra. Aircraft Description
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
VI
Curtiss-Wright XP-55 Ascender
Curtiss-Wright XP-55 Ascender
|
11 | 5 | 6 | 0 | ||||||||||||||||
|
Designed as a promising interceptor fighter with a canard configuration. The first prototype took to the air in July 1943. The tests dragged on until December 1944 when the project was recognized as having no prospects. Aircraft Description
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
VI

Kawasaki Ki-61 Hien
Kawasaki Ki-61 Hien
|
28 | 14 | 11 | 0 | ||||||||||||||||
|
First flew in December 1941. Different modifications of the Ki-61 were extensively used during the Pacific War from the early 1943 and through the final days of World War II. Over 3,000 aircraft were built. Aircraft Description
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
VI

P-39Q-15 Airacobra
P-39Q-15 Airacobra
|
32 | 13 | 12 | 0 | ||||||||||||||||
|
A significant number of the P-39 Airacobra were supplied to the U.S.S.R. under the Lend-Lease program. The P-39Q-15 was a lighter version that had no wing-mounted weapons. Aircraft Description
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
VI

Kawasaki Ki-88
Kawasaki Ki-88
|
8 | 3 | 5 | 0 | ||||||||||||||||
|
Designed for the Imperial Japanese Army Air Force as a heavily armed interceptor. Development was discontinued during the prototype stage. Aircraft Description
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
VI

Supermarine Spitfire V DB 605
Supermarine Spitfire V DB 605
|
225 | 105 | 18 | 1 | ||||||||||||||||
|
During trials of captured Spitfires in Germany, one aircraft was equipped with a German DB 605 engine. It was later destroyed in an Allied air raid. Aircraft Description
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
VI

Mitsubishi A6M5 Zero
Mitsubishi A6M5 Zero
|
26 | 19 | 13 | 0 | ||||||||||||||||
|
This modification of the A6M confronted Allied fighters until the final days of WWII. A total of 10,449 aircraft of all variants were produced. Aircraft Description
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
VI

Messerschmitt Bf 109 F Friedrich
Messerschmitt Bf 109 F Friedrich
|
14 | 7 | 6 | 0 | ||||||||||||||||
|
Developed in 1940, the Bf 109 F outperformed the earlier Bf 109 E due to lighter armament, improved aerodynamics, and a more powerful engine. Aircraft Description
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
VII

Yakovlev Yak-3
Yakovlev Yak-3
|
9 | 4 | 6 | 0 | ||||||||||||||||
|
Created in 1943 on the basis of the Yak-1. One of the best Soviet fighters of 1944–1945. A total of 4,848 aircraft of this type were built. Aircraft Description
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
VII

Lavochkin La-7
Lavochkin La-7
|
16 | 6 | 13 | 0 | ||||||||||||||||
|
A further development of the famous La-5 featuring enhanced aerodynamics. A total of 5,753 aircraft were produced from 1944 through 1945. Aircraft Description
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
VII

North American P-51K Mustang
North American P-51K Mustang
|
2 | 1 | 8 | 0 | ||||||||||||||||
|
Dallas-built version of the P-51D. After World War II, it was exported to various countries including China, where it served in the Chinese Nationalist Air Force. A total of 1,500 aircraft were built. Aircraft Description
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
VII

Yakovlev Yak-3RD
Yakovlev Yak-3RD
|
21 | 7 | 10 | 0 | ||||||||||||||||
|
Modification of the mass-produced Yak-3 featuring an auxiliary liquid-fuel rocket engine and a single cannon. The prototype underwent trials in 1944–1945. Aircraft Description
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
VII

Lavochkin La-9RD
Lavochkin La-9RD
|
4 | 1 | 3 | 0 | ||||||||||||||||
|
Developed on the basis of the mass-produced La-9 to explore the capabilities of ramjet engines. Several prototypes were produced and tested. Aircraft Description
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
VII

Reggiane Re.2005 Sagittario
Reggiane Re.2005 Sagittario
|
4 | 1 | 1 | 0 | ||||||||||||||||
|
Produced during the later years of World War II, this single-seat fighter saw action in many famous battles. A total of 48 aircraft were built. Aircraft Description
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
VII

Supermarine Spitfire IX
Supermarine Spitfire IX
|
42 | 11 | 7 | 0 | ||||||||||||||||
|
One of the most successful modifications of the famous British fighter. A total of 5,656 aircraft were built. Aircraft Description
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
VII
Mitsubishi A7M Reppu
Mitsubishi A7M Reppu
|
45 | 20 | 9 | 0 | ||||||||||||||||
|
Developed in 1942–1945 for the Imperial Japanese Navy as a successor to the A6M. Only 8 prototypes were produced and tested by the end of the war. Aircraft Description
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
VIII

Lavochkin La-9
Lavochkin La-9
|
21 | 8 | 6 | 0 | ||||||||||||||||
|
An all-metal fighter created on the basis of the La-7 featuring a wider combat radius and more powerful weapons. Used during the Korean War. Aircraft Description
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
VIII

Yakovlev Yak-15
Yakovlev Yak-15
|
11 | 4 | 3 | 0 | ||||||||||||||||
|
The first jet-powered fighter to enter service with the Soviet Air Force. Developed on the basis of the Yak-3 in 1946. A total of 280 aircraft were produced. Aircraft Description
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
VIII

De Havilland DH.100 Vampire F.1
De Havilland DH.100 Vampire F.1
|
2 | 1 | 3 | 0 | ||||||||||||||||
|
The first mass-produced modification of the DH.100 Vampire featuring the Goblin I engine. Entered service in April 1945. A total of 40 aircraft of the early F.1 series were built, but they did not see combat due to the end of World War II. Aircraft Description
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
IX

Yakovlev Yak-19
Yakovlev Yak-19
|
46 | 21 | 10 | 0 | ||||||||||||||||
|
Developed in 1946. The first Soviet jet-powered fighter of classic design. Only two prototypes were built. Aircraft Description
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| Multirole Fighters 25 | 411 | 208 | ||||||||||||||||||
|
I

Polikarpov I-5
Polikarpov I-5
|
30 | 16 | 26 | 1 | ||||||||||||||||
|
One of the main fighter aircraft of the Red Army Air Force in the early 1930s. Used during World War II on a limited basis. Aircraft Description
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
II

Curtiss Hawk III
Curtiss Hawk III
|
1 | 1 | 3 | 0 | ||||||||||||||||
|
An export version of the Curtiss BF2C-1. A total of 137 aircraft were built for the Air Forces of China, Argentina, Turkey, and Thailand. Licensed for production in China. Aircraft Description
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
II

Curtiss F11C-2
Curtiss F11C-2
|
2 | 1 | 2 | 1 | ||||||||||||||||
|
Carrier-based fighter-bomber. A total of 28 aircraft were built for the U.S. Navy from 1932 through 1933. Exported as the Hawk II. Aircraft Description
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
II

Polikarpov I-15
Polikarpov I-15
|
3 | 2 | 14 | 0 | ||||||||||||||||
|
Early 1930s high specification biplane fighter. Saw extensive action in conflicts beyond the borders of the U.S.S.R. Aircraft Description
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
II

Polikarpov I-5 ShKAS
Polikarpov I-5 ShKAS
|
142 | 83 | 30 | 1 | ||||||||||||||||
|
To increase firepower, the PV-1 machine guns on some of the I-5 fighters were replaced by the ShKAS, which had higher rate of fire. Aircraft Description
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
III

Kochyerigin-Yatsenko DI-6i
Kochyerigin-Yatsenko DI-6i
|
5 | 3 | 8 | 0 | ||||||||||||||||
|
Developed as a two-seat multirole fighter capable of engaging single-seat fighters in maneuvering combat. Its first flight took place in September 1934. The aircraft did not see active combat service. A total of 223 modifications of the DI-6 were built. Aircraft Description
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
III

Blackburn Skua Mk. 1
Blackburn Skua Mk. 1
|
1 | 1 | 2 | 1 | ||||||||||||||||
|
An early modification of the Blackburn Skua, a British fighter-bomber powered by the Mercury IX engine. Due to a shortage of these engines, serial models were equipped with other available motors. Aircraft Description
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
III

Polikarpov I-16 (early mod.)
Polikarpov I-16 (early mod.)
|
18 | 9 | 14 | 0 | ||||||||||||||||
|
Developed in the early 1930s as a high-speed fighter. Used in Spain in 1936, during the Battles of Khalkhyn Gol in 1939, and through World War II. Aircraft Description
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
IV

Polikarpov I-16 (late mod.)
Polikarpov I-16 (late mod.)
|
3 | 3 | 3 | 0 | ||||||||||||||||
|
Modification of the I-16 featuring more powerful weapons and improved performance. Aircraft Description
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
IV

Polikarpov I-16 Type 29
Polikarpov I-16 Type 29
|
1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | ||||||||||||||||
|
Last mass-produced modification of the Polikarpov I-16. First flew in 1940. The main difference from its predecessors was it had no guns in the wings, but carried a synchronized large-caliber machine gun. Aircraft Description
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
IV

Borovkov-Florov I-207/4
Borovkov-Florov I-207/4
|
2 | 1 | 1 | 2 | ||||||||||||||||
|
The last developed version of the I-207 fighter. The aircraft was supposed to have the properties of both high-speed monoplanes and maneuverable biplanes. The prototype was built by the spring of 1941, but the project was discontinued. Aircraft Description
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
IV

Arado Ar 197
Arado Ar 197
|
63 | 25 | 14 | 2 | ||||||||||||||||
|
The last German biplane fighter. Designed for naval operations for the never-completed aircraft carrier Graf Zeppelin. Aircraft Description
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
IV

Hawker Hurricane Mk I
Hawker Hurricane Mk I
|
20 | 9 | 9 | 0 | ||||||||||||||||
|
The main British fighter type of early World War II. The prototype first flew in November 1935. Widely used in the French campaign in 1940 and massively used in the Battle of Britain. Aircraft Description
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
IV

Lavochkin LaGG-3 series 4
Lavochkin LaGG-3 series 4
|
17 | 9 | 18 | 1 | ||||||||||||||||
|
The LaGG-3 series 4 was fitted with a modified engine and carried more powerful armament compared to the early LaGG-3s. Extensively used in the initial period of World War II. Aircraft Description
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
V

Hawker Hurricane IID
Hawker Hurricane IID
|
2 | 1 | 3 | 0 | ||||||||||||||||
|
Developed in 1941 as a specialized anti-tank aircraft on the basis of the Hawker Hurricane fighter. Aircraft Description
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
V

Hawker Hurricane Mk II
Hawker Hurricane Mk II
|
48 | 17 | 10 | 1 | ||||||||||||||||
|
The Hurricane Mk II entered service in 1940. Compared to the early fighter variants, it was equipped with a more powerful engine, and its armament was gradually enhanced. This modification remained in production until 1944 and was also built in Canada. Aircraft Description
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
V

Yakovlev Yak-7
Yakovlev Yak-7
|
22 | 10 | 14 | 0 | ||||||||||||||||
|
Developed in 1941 on the basis of the Yak-7UTI flight trainer. A total of 6,399 fighters of various modifications were built, including training aircraft. Aircraft Description
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
V

Grumman F4F Wildcat
Grumman F4F Wildcat
|
8 | 5 | 9 | 1 | ||||||||||||||||
|
The best U.S. carrier-based fighter at the start of the war with Japan. Used from the outset through the end of the war. Aircraft Description
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
V

Republic XP-44 Rocket
Republic XP-44 Rocket
|
8 | 4 | 6 | 2 | ||||||||||||||||
|
A further development of the P-43 Lancer featuring a more powerful Pratt & Whitney R-2180 engine. Development was discontinued due to the decision of the Republic Aviation Corporation to focus on building a more promising P-47 fighter. Aircraft Description
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
V

Lavochkin LaGG-3 series 34
Lavochkin LaGG-3 series 34
|
1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | ||||||||||||||||
|
Modification of the LaGG-3 fighter. Used extensively for destroying aerial and ground targets, including armored targets. Aircraft Description
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
V

Curtiss P-40 M-105
Curtiss P-40 M-105
|
1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | ||||||||||||||||
|
As the U.S.S.R. lacked spare Allison engines, a few P-40 fighters were fitted with Soviet M-105 engines. Aircraft Description
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
V

Yakovlev Yak-7 M-82
Yakovlev Yak-7 M-82
|
4 | 1 | 1 | 0 | ||||||||||||||||
|
In the summer of 1941, an attempt to install an M-82A engine on the Yak-7 was made. The aircraft went through a number of changes in the design and composition of its weapons, but could not achieve the specified flight characteristics for technical reasons. Only one development prototype was made. Aircraft Description
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
VI

Avia S-199 Sakeen
Avia S-199 Sakeen
|
6 | 2 | 3 | 1 | ||||||||||||||||
|
Developed in Czechoslovakia after World War II on the basis of the German Messerschmitt Bf 109. In 1948, some of the S-199's were purchased by Israel, which later used them during the Arab-Israeli conflict. These aircraft became the first combat-ready fighters of the arising Israeli Air Force. Aircraft Description
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
VI
Ilyushin IL-1
Ilyushin IL-1
|
1 | 1 | 2 | 1 | ||||||||||||||||
|
Designed as an armored low- and mid-altitude fighter capable of engaging enemy aircraft in a maneuvering combat. The project was discontinued due to the achievement of air superiority by the Soviet Air Force in 1944. Aircraft Description
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
VII
Mitsubishi J4M Senden
Mitsubishi J4M Senden
|
2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | ||||||||||||||||
|
Designed as a high-speed interceptor fighter. Delayed development made the Imperial Japanese Navy discontinue the project in favor of the J7W1. Aircraft Description
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| Heavy Fighters 18 | 294 | 121 | ||||||||||||||||||
|
III

Focke-Wulf Fw 57
Focke-Wulf Fw 57
|
2 | 1 | 3 | 4 | ||||||||||||||||
|
Twin-engine heavy fighter. One of the first Zerstörer concepts developed for the Luftwaffe. Aircraft Description
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
III

Dornier Do 17 Z-7 Kauz
Dornier Do 17 Z-7 Kauz
|
1 | 1 | 2 | 3 | ||||||||||||||||
|
Developed on the basis of the Do 17 Z bomber as a heavy night fighter. Featured more powerful weapons and reduced bomb load. Aircraft Description
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
III

PZL P.38 Wilk
PZL P.38 Wilk
|
2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||||||||||||||||
|
Developed from 1934 as a multipurpose aircraft with the ability to perform as both a fighter and a ground forces support aircraft. Only two prototypes were built and tested before World War II. Aircraft Description
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
IV

Messerschmitt Bf 110 B
Messerschmitt Bf 110 B
|
4 | 3 | 7 | 2 | ||||||||||||||||
|
Created as a "strategic fighter," a concept popular in the interwar period. Successfully used in campaigns in Poland, France, and Norway. Aircraft Description
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
IV

Messerschmitt Bf 110 C-6
Messerschmitt Bf 110 C-6
|
2 | 2 | 5 | 0 | ||||||||||||||||
|
Modification of the serial Bf 110 equipped with a 30 mm MK-101 antitank cannon. A total of 12 aircraft were produced during May–July 1940. Aircraft Description
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
IV

Bristol Blenheim F
Bristol Blenheim F
|
10 | 4 | 5 | 2 | ||||||||||||||||
|
Modification of the Blenheim bomber into a long-range fighter or night fighter. A total of 60 aircraft were modified. Aircraft Description
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
V

Bristol Beaufighter
Bristol Beaufighter
|
77 | 32 | 17 | 2 | ||||||||||||||||
|
First flew in July 1939. Used as a long-range fighter and night fighter. A total of 5,928 aircraft were built. Aircraft Description
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
V

SNCASE SE 100
SNCASE SE 100
|
34 | 13 | 14 | 0 | ||||||||||||||||
|
A project for a heavy fighter carrying powerful offensive and defensive armament. First flew in March 1939. The development was discontinued due to the occupation of France in 1940. Aircraft Description
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
V

Bristol Beaufighter V
Bristol Beaufighter V
|
40 | 16 | 11 | 0 | ||||||||||||||||
|
The Beaufighter V modification. Aircraft Description
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
V

Messerschmitt Bf 110 E
Messerschmitt Bf 110 E
|
6 | 3 | 7 | 1 | ||||||||||||||||
|
A forced upgrade of the 110 by the Messerschmitt company due to the failed creation of the Me 210. Used both offensively and as a night fighter. Aircraft Description
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
V

Messerschmitt Me 210
Messerschmitt Me 210
|
4 | 2 | 6 | 2 | ||||||||||||||||
|
Heavy fighter designed to replace the Bf 110. Entered limited service with the Luftwaffe. Also licensed for production in Hungary. Aircraft Description
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
V

Kawasaki Ki-45 Toryu
Kawasaki Ki-45 Toryu
|
49 | 20 | 10 | 2 | ||||||||||||||||
|
Developed as a long-range fighter for Southeast Asia and the Pacific. Saw combat from the summer of 1942 and was extensively used before the end of the war in the Japanese anti-aircraft defense to counter U.S. heavy bombers. Aircraft Description
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
VI

De Havilland 98 Mosquito FB 26
De Havilland 98 Mosquito FB 26
|
3 | 2 | 6 | 2 | ||||||||||||||||
|
Canadian-built version of the Mosquito FB VI. A significant number of the Mosquito FB Mk.26 were delivered to China after the end of the war against Japan. Aircraft Description
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
VI

Grumman XP-50
Grumman XP-50
|
1 | 1 | 2 | 0 | ||||||||||||||||
|
Developed as a twin-engine interceptor for the U.S. Army Air Force. First flew in February 1941. Only one prototype was built. Never entered service. Aircraft Description
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
VI

Vultee XP-54 Swoose Goose
Vultee XP-54 Swoose Goose
|
8 | 2 | 8 | 0 | ||||||||||||||||
|
Designed for the U.S. Army Air Forces as a modern interceptor with top-notch flight characteristics. Two prototypes were built, and the aircraft made its maiden flight on January 15, 1943. However, problems with its intended engine and a series of modifications requested by the customer significantly reduced the aircraft's potential characteristics. As a result, the project was canceled. Aircraft Description
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
VI
Kawasaki Ki-102
Kawasaki Ki-102
|
4 | 1 | 3 | 1 | ||||||||||||||||
|
Developed in several versions to be used against both aerial and ground targets and to replace the Ki-45. Saw limited action before the end of the war. Aircraft Description
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
VI

Messerschmitt Me 410 Hornisse
Messerschmitt Me 410 Hornisse
|
45 | 16 | 9 | 1 | ||||||||||||||||
|
Heavy fighter-bomber, a further development of the Zerstörer concept. Used mainly on the Western Front. Aircraft Description
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
VII

Arsenal VB 10
Arsenal VB 10
|
2 | 1 | 2 | 0 | ||||||||||||||||
|
Development was started before the occupation of France. The prototype first flew in the summer of 1945. A total of 200 aircraft were ordered. However, due to the development of jet aircraft and decreasing interest in the project, only 2 prototypes and a series of 4 aircraft were built. Aircraft Description
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| Attack Aircraft 15 | 164 | 81 | ||||||||||||||||||
|
II

Fieseler Fi 98
Fieseler Fi 98
|
2 | 1 | 1 | 3 | ||||||||||||||||
|
Designed for close support of ground forces. The only completed prototype underwent trials in 1935. Never entered mass production. Aircraft Description
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
II
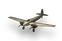
Tomashevich Pegasus
Tomashevich Pegasus
|
1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | ||||||||||||||||
|
Designed as a technologically simple and low-cost strike aircraft suitable for mass production. Several prototypes were built. Aircraft Description
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
II

Henschel Hs 123
Henschel Hs 123
|
1 | 1 | 6 | 2 | ||||||||||||||||
|
First flew in May 1935. Successfully used for close air support during the Spanish Civil War and World War II. A total of about 260 aircraft were built. Aircraft Description
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
III

Kochyerigin BSh-1
Kochyerigin BSh-1
|
22 | 11 | 8 | 7 | ||||||||||||||||
|
In 1936, the Soviet Union purchased from the U.S. a production license for the Vultee V-11 attack bomber. Redesigned as the BSh-1, it underwent trials in 1937–1939. Aircraft Description
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
III

CAC CA-1 Wirraway
CAC CA-1 Wirraway
|
19 | 10 | 6 | 8 | ||||||||||||||||
|
Designed to support ground forces. Used by the Royal Australian Air Forces in the Pacific during World War II. A total of 755 aircraft were built in 1939–1946. Aircraft Description
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
III

Kochyerigin TSh-3
Kochyerigin TSh-3
|
15 | 8 | 3 | 8 | ||||||||||||||||
|
Developed in the early 1930s as a heavy armored attack aircraft for the Red Army Air Force. Aircraft Description
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
III

Blohm und Voss Ha 137 V1
Blohm und Voss Ha 137 V1
|
1 | 1 | 0 | 2 | ||||||||||||||||
|
The initial prototype of Blohm und Voss Ha 137, first flown in April 1935. As the main difference from later modifications, it was equipped with the BMW 132 engine. Aircraft Description
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
IV

Kochyerigin Sh (LBSh)
Kochyerigin Sh (LBSh)
|
24 | 10 | 2 | 10 | ||||||||||||||||
|
Developed as a high-speed two-seat attack aircraft with two prototypes produced. Aircraft Description
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
IV

Henschel Hs 129 А
Henschel Hs 129 А
|
3 | 1 | 1 | 2 | ||||||||||||||||
|
Early version of the armored Hs 129 attack aircraft fitted with Argus engines. A small series of aircraft was used mainly for pilot training. Aircraft Description
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
IV

Focke-Wulf Fw 189 C Eule
Focke-Wulf Fw 189 C Eule
|
4 | 3 | 4 | 3 | ||||||||||||||||
|
Armored attack aircraft based on the famous Fw 189 reconnaissance aircraft. Several prototypes underwent trials in 1939–1940. Aircraft Description
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
V

IL-2 with rear gunner
IL-2 with rear gunner
|
15 | 8 | 3 | 7 | ||||||||||||||||
|
During frontline trials, several attempts were made to modify the IL-2 by adding a rear gunner position. Aircraft Description
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
V

Junkers Ju 87 G Stuka
Junkers Ju 87 G Stuka
|
10 | 5 | 2 | 2 | ||||||||||||||||
|
Attack modification of the iconic Ju 87 Stuka dive bomber featuring enhanced armament and armor. Aircraft Description
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
VI

Ilyushin IL-2 two-seat
Ilyushin IL-2 two-seat
|
10 | 6 | 1 | 9 | ||||||||||||||||
|
A later version of the IL-2, configured with a rear gunner. Became the most widely produced attack aircraft of World War II. Aircraft Description
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
VI

Junkers Ju 88 P
Junkers Ju 88 P
|
31 | 13 | 4 | 3 | ||||||||||||||||
|
Anti-tank modification of the Ju 88 bomber. Several dozen aircraft equipped with different armament variants were built. Aircraft Description
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
VIII

SNCAC NC 1070
SNCAC NC 1070
|
6 | 2 | 1 | 3 | ||||||||||||||||
|
Attack aircraft designed for a wide range of missions. The single completed prototype was tested in 1947–1948. Aircraft Description
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| Bombers 19 | 918 | 400 | ||||||||||||||||||
|
III

Potez 540
Potez 540
|
3 | 1 | 0 | 3 | ||||||||||||||||
|
A French air cruiser of the first half of the 1930s. Was called up to perform a wide range of missions: from reconnaissance to strikes on enemy positions. Proved successful in the early stages of the Spanish Civil War. By the beginning of active hostilities against Germany, the planes were considered obsolete and removed from combat units. Aircraft Description
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
III

Junkers Ju 86 E
Junkers Ju 86 E
|
15 | 7 | 3 | 11 | ||||||||||||||||
|
Due to problems with the diesel engines on the early Ju 86, it was decided to replace them with the radial BMW 132. The new modification—the Ju 86 E—served with the Luftwaffe until it was replaced by more advanced He 111 bombers. Aircraft Description
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
III

Bristol Blenheim Mk.IV (early mod.)
Bristol Blenheim Mk.IV (early mod.)
|
43 | 22 | 2 | 15 | ||||||||||||||||
|
Developed by the Bristol company as Type 149. Featured a lengthened nose, which provided more comfortable conditions for a navigator. The first several Blenheim Mk.IVs inherited the defensive armament of the Blenheim Mk.I. Aircraft Description
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
III

Arkhangelsky/Tupolev SB
Arkhangelsky/Tupolev SB
|
18 | 9 | 1 | 9 | ||||||||||||||||
|
The main Soviet pre-war medium bomber. First took to the air in 1934. Extensively used in the late 1930s and in early Word War II. A total of 7,000 aircraft of various modifications were built. Aircraft Description
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
IV

Arkhangelsky Ar-2
Arkhangelsky Ar-2
|
37 | 16 | 2 | 10 | ||||||||||||||||
|
A drastic modification of the SB bomber built with the aim of improving its combat performance. First flew in 1940. A total of about 200 aircraft were built and saw combat along with the SB. Aircraft Description
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
IV

Dornier Do 17 Z
Dornier Do 17 Z
|
28 | 20 | 1 | 12 | ||||||||||||||||
|
The last and most advanced version of the Do 17 bomber. The prototype first took to the air in March 1938. It featured an absolutely new cockpit design, new engines, and enhanced defensive armament. A total of roughly 500 Do 17 Z aircraft in several versions were built. Aircraft Description
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
IV

Heinkel He 111 H-2
Heinkel He 111 H-2
|
65 | 28 | 2 | 11 | ||||||||||||||||
|
A modification of one of the most well-known German World War II bombers. The He 111 H-2 entered mass production in September 1939. This aircraft differed from the early Не 111 in the engines and enhanced defensive armament. Over 500 aircraft of the H-2 series were produced. Aircraft Description
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
V

Boeing B-17D Flying Fortress
Boeing B-17D Flying Fortress
|
19 | 11 | 1 | 7 | ||||||||||||||||
|
The B-17D modification was developed in February 1941. Most of these bombers were sent to the U.S. air bases in the Pacific, where the beginning of the war with Japan found them. Aircraft Description
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
V

Junkers Ju 88 A
Junkers Ju 88 A
|
78 | 39 | 2 | 18 | ||||||||||||||||
|
The most mass-produced modification of the Ju 88. Mass production started in March 1939, and by 1940–1941, the Ju 88 A became the main bomber type in the Luftwaffe. The aircraft was widely used on all fronts and was also supplied to the allies of Germany. Aircraft Description
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
V

Petlyakov Pe-2
Petlyakov Pe-2
|
37 | 18 | 2 | 8 | ||||||||||||||||
|
The main Soviet tactical bomber of World War II. The prototype first flew in December 1939. Over 11,000 Pe-2s of various modifications were built and saw extensive action throughout World War II. Aircraft Description
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
VI

Petlyakov Pe-2 M-82
Petlyakov Pe-2 M-82
|
25 | 10 | 4 | 6 | ||||||||||||||||
|
A modification of the Pe-2 bomber equipped with new engines. The prototype was built in the fall of 1942. Due to the shortage of engines that were in great demand for developing the Lavochkin fighters, only 32 aircraft were built, but saw limited combat. Aircraft Description
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
VI

Avro Lancaster B Mk.III
Avro Lancaster B Mk.III
|
3 | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||||||||||||||||
|
A legendary British heavy bomber from World War II, capable of carrying up to 12,000 pounds of bomb load. A total of 7,377 of these aircraft were produced. Aircraft Description
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
VI

Douglas A-26B Invader
Douglas A-26B Invader
|
186 | 84 | 5 | 9 | ||||||||||||||||
|
Developed as an attack bomber to replace the Douglas A-20 Havoc serving the U.S. Air Force. The A-26B was the first aircraft in the series to enter mass production. A significant number of modifications were built based on the A-26B. Aircraft Description
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
VI

Boeing B-17G Flying Fortress
Boeing B-17G Flying Fortress
|
109 | 44 | 4 | 6 | ||||||||||||||||
|
The most mass-produced version of the Flying Fortress with significantly enhanced defensive armament. Extensively used in the strategic bombing campaign against Germany. Aircraft Description
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
VI

Dornier Do 217 M
Dornier Do 217 M
|
44 | 17 | 1 | 10 | ||||||||||||||||
|
The Do 217 M was a variant of the mass-produced Do 217 K with the DB 603 engine instead of the BMW 801 that was in great demand for fighters. Both bomber variants were used mainly on the Western Front. Aircraft Description
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
VII

Consolidated B-32 Dominator
Consolidated B-32 Dominator
|
53 | 22 | 4 | 8 | ||||||||||||||||
|
Designed to the same specifications as the well-known B-29 Superfortress. However, the development of the B-32 was slow due to technical issues. Saw limited action during raids on Japan before the end of the war. Aircraft Description
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
VII

Mitsubishi G4M2 Model 24
Mitsubishi G4M2 Model 24
|
4 | 1 | 1 | 2 | ||||||||||||||||
|
Second iteration of one of the most widely produced Japanese bombers in World War II. Aircraft Description
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
VIII

Boeing B-29C Superfortress
Boeing B-29C Superfortress
|
6 | 2 | 4 | 6 | ||||||||||||||||
|
One of the most iconic bombers of World War II. 5,000 re-engined B-29C were ordered. After the end of World War II, the order was canceled. Aircraft Description
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
VIII

Myasishchev RB-17
Myasishchev RB-17
|
145 | 48 | 2 | 10 | ||||||||||||||||
|
Project for a high-speed reconnaissance bomber. Developed in 1945–1946 with the use of the German Jumo 004 engine. Development was discontinued in early 1946 as the Myasishchev design bureau was closed. Aircraft Description
|
||||||||||||||||||||